Discover the evolution of global trade, from the Silk Road to today’s digital economy, driven by technology and emerging markets.
Table of Contents

Prefer to listen? Enjoy the audio version of this article
Curated audio version | Audio powered by AI
Global trade has undergone significant transformations over the centuries, shaped by technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and economic developments. From the ancient Silk Road connecting the East and West to the modern-day interconnected global economy, trade has played a crucial role in fostering international relations, driving economic growth, and shaping cultures around the world. As we look to the future, the evolution of global trade continues to be influenced by factors such as digitalization, sustainability concerns, and the rise of emerging markets, highlighting the dynamic nature of this fundamental aspect of human interaction.
The Origins of Early Global Trade

Trade in ancient civilizations
Trade in ancient civilizations was a pivotal aspect of their economic and cultural development. Early trade routes like the Silk Road and the Spice Trade played a crucial role in connecting different regions and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. The Silk Road, for example, was a network of trade routes that linked the East and West, enabling the exchange of silk, spices, precious metals, and other valuable commodities.
Medieval trade networks
Medieval trade networks, such as the Hanseatic League and Mediterranean trade, had a significant impact on regional economies. The Hanseatic League facilitated trade across Northern Europe, while Mediterranean trade connected Europe, Africa, and Asia, fostering economic prosperity and cultural exchange. These networks not only boosted economies but also facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, and cultural practices, enriching the societies involved.
The Age of the Great Seas and Colonialism
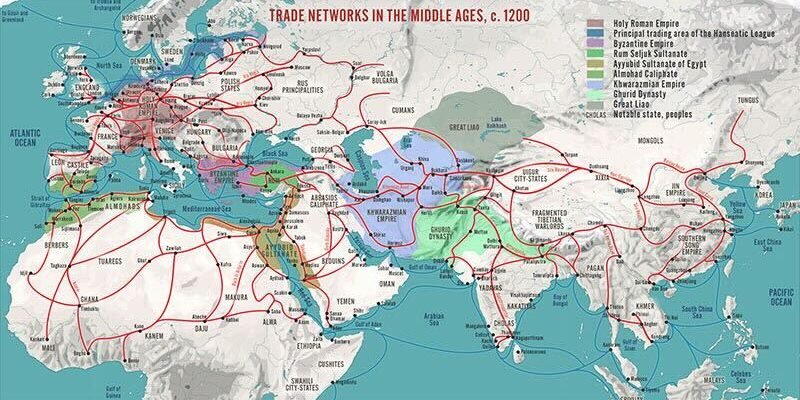
The opening of new routes
The geographic discoveries of the 15th to 17th centuries had a profound impact on global trade, with explorers like Columbus and Magellan opening new sea routes to Asia, Africa, and the Americas. These discoveries led to the Columbian Exchange, which reshaped global trade by facilitating the exchange of crops, animals, and goods on an unprecedented scale.
Colonial trade
Colonial trade during the age of colonialism significantly impacted global trade patterns by leading to the global transfer of resources and wealth. European colonial powers exploited resources from their colonies, leading to the establishment of trade routes that transported goods between the colonies and Europe, fueling the industrial revolution in Europe at the expense of the colonies.
The Industrial Revolution and the globalization of trade

The impetus of the industrial revolution
The Industrial Revolution, beginning in the late 18th century, marked a shift from agrarian economies to industrialized ones. Technological innovations, urbanization, and transportation advancements greatly increased production capacity and expanded markets, laying the foundation for the modern interconnected global economy.
The protectionism versus free trade debate
The late 19th to early 20th century was characterized by debates between protectionism and free trade. Countries implemented protectionist measures to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, while advocates of free trade argued for minimal restrictions to promote economic efficiency and consumer choice.
Reorganization of global trade after World War II
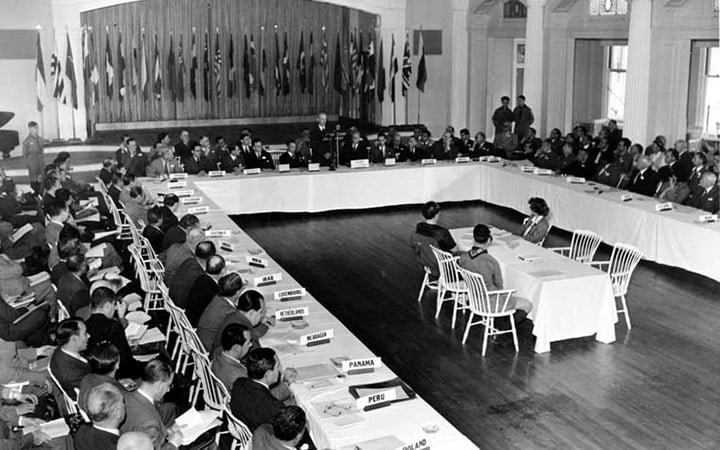

Establishment of the Bretton Woods system
The Bretton Woods system, established after World War II, reorganized global trade by promoting economic stability and facilitating international trade. The system introduced fixed exchange rates tied to the U.S. dollar and established institutions like the IMF and World Bank, which laid the foundation for the post-war economic order.
Globalization and the rise of international trade organizations
The formation of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and regional trade agreements like the European Union and NAFTA played crucial roles in shaping international trade relations, reducing trade barriers, and promoting economic integration among member countries.
Global trade challenges and opportunities in the twenty-first century

Digitalization and trade
Digitalization and e-commerce have revolutionized traditional trade patterns by enabling businesses to reach a global audience more easily and efficiently. The integration of digital technologies has created new business models, streamlined supply chains, and transformed international commerce, presenting both challenges and opportunities for businesses.
Globalization and vulnerability of supply chains
The COVID-19 pandemic and geopolitical tensions have exposed the vulnerabilities of global supply chains. Companies are now reevaluating their strategies to mitigate risks and enhance resilience, considering factors like diversification of suppliers and investment in digital technologies for supply chain visibility.
Return of trade protectionism
The return of protectionism in recent years has led to trade wars that have disrupted established supply chains and increased uncertainty in the global economy. The rise of protectionism highlights the challenges of globalization and economic interdependence, with countries prioritizing national interests over global cooperation.

Sustainable development and trade
Sustainable development and trade are becoming increasingly intertwined as environmental concerns reshape global trade practices. Green trade initiatives, such as carbon pricing and eco-labeling, are gaining traction as businesses and governments seek to reduce their carbon footprint and promote sustainable production and consumption patterns.
Future outlook

Technological advances and the future of trade
Technological advances, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain, are poised to revolutionize future global trade by enhancing automation, optimizing supply chains, and improving transparency and efficiency in transactions.
Multilateral cooperation and emerging markets
Emerging market countries are becoming increasingly significant players in global trade. Their participation, supported by multilateral cooperation, is essential for driving economic growth, fostering innovation, and building a more interconnected and prosperous global economy.
Conclusion

Global trade has evolved dramatically, influenced by technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and economic developments. The interplay between protectionism and free trade, the integration of sustainability principles, and the impact of technological advancements and multilateral cooperation are crucial in determining the future of international trade. As we move forward, the continued evolution of global trade will be shaped by technological progress, the active involvement of emerging markets, and strengthened multilateral collaboration, all of which will have far-reaching implications for the global economy.
FAQs
-
What was the Silk Road, and why was it important?
Answer: The Silk Road was a major trade route connecting ancient China with Mediterranean countries, facilitating the exchange of goods (like silk and spices), culture, and ideas between the East and the West. It played a crucial role in the early stages of globalization and helped develop trade across continents.
-
What is the Bretton Woods system?
Answer: The Bretton Woods system was an international monetary framework established after World War II. It created a system of fixed exchange rates and led to the establishment of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the World Bank, which aimed to stabilize global financial systems and support post-war economic recovery.
-
How has globalization impacted modern trade?
Answer: Globalization has accelerated economic integration between countries, enabling the free flow of goods, services, capital, technology, and labor across borders. This has expanded global trade but also presented challenges, such as economic inequality and environmental concerns.
-
How did the Industrial Revolution change global trade?
Answer: The Industrial Revolution introduced mechanized production, large-scale factories, and new transportation methods (like railways and steamships), significantly increasing production efficiency and trade volume. This shift marked the beginning of modern global trade by enabling faster and cheaper movement of goods worldwide.
-
Why were global supply chains disrupted during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Answer: Global supply chains were disrupted during the pandemic due to their complexity and interdependence. The pandemic caused production halts, logistics disruptions, and demand shifts, revealing the vulnerabilities in the global trade system’s ability to adapt quickly to sudden changes.
-
What future technologies might impact global trade?
Answer: Technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), blockchain, the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G networks, and automation are expected to significantly impact global trade. These technologies will enhance supply chain management, increase data transparency, reduce transaction costs, and drive the automation and smartization of trade processes.
-
What is trade protectionism, and how does it affect global trade?
Answer: Trade protectionism involves using tariffs, quotas, subsidies, and other measures to protect a country’s economy from foreign competition. In recent years, the rise of protectionism has led to international trade conflicts and trade wars, which negatively affect the stability and growth of the global trade system.












