Explore sustainability in globalization, focusing on environmental impact and solutions that drive a more sustainable and responsible global future.
Global Shifts
Navigating the Future of a Connected World
As the world becomes more interconnected, the forces driving globalization have far-reaching impacts on economies, businesses, and societies. This series dives deep into the core elements shaping today’s global landscape, from technological innovation and economic integration to cultural exchange and environmental sustainability.
Through a comprehensive exploration of these topics, “Global Shifts” offers thought-provoking insights into how businesses can adapt to this rapidly changing environment. Whether you’re a leader aiming to stay ahead of global trends or a professional seeking to understand the shifting dynamics of global trade, this series provides the essential knowledge to navigate the future of globalization.
Series
- Episode1.Globalization 101: Understanding the Basics
- Episode2.Economic Globalization: Trade and Investment Flows
- Episode3.Technological Globalization: The Role of Digitalization
- Episode4.Cultural Globalization: Cross-cultural Exchange and Influence
- Episode5.Political Globalization: Global Governance and Multilateralism
- Episode6.Sustainability in Globalization: Environmental Impact and Solutions
- Episode7.Global Supply Chains: Challenges and Opportunities
- Episode8.The Future of Globalization: Trends and Predictions
- Episode9.Challenges of Globalization: Inequality and Social Impacts
- Episode10.Globalization and Innovation: How Companies Stay Competitive
Table of Contents

Prefer to listen? Enjoy the audio version of this article
Curated audio version | Audio powered by AI
The Intersection of Globalization and Sustainability

Globalization has significantly shaped the modern world, enabling countries to connect through trade, communication, and cultural exchange. While globalization has contributed to economic growth and poverty reduction, it has also led to increased environmental degradation. The rapid expansion of global trade, industrialization, and resource consumption has had profound consequences for the planet. Addressing these challenges requires a rethinking of how sustainability can be integrated into the processes of globalization.
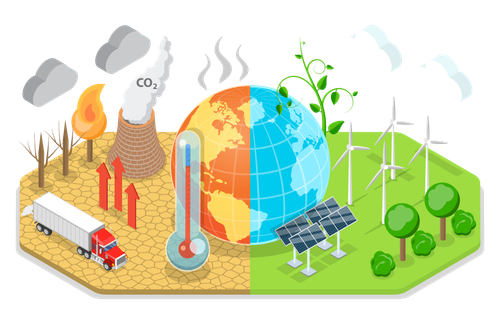
Overview of Globalization’s Environmental Impact
Globalization has accelerated the pace at which goods are produced, transported, and consumed. This increased activity has led to higher levels of greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and pollution. International trade often relies on long-distance transportation, particularly shipping and aviation, which are major contributors to carbon emissions. Additionally, the demand for raw materials has intensified resource extraction, putting pressure on ecosystems around the world. As a result, globalization has become a significant driver of environmental change, and without appropriate measures, its impacts could further exacerbate the ongoing climate crisis.

The Importance of Integrating Sustainability into Globalization
As the global community becomes more aware of the environmental consequences of economic activities, there is a growing recognition that sustainability must be embedded within the processes of globalization. Sustainable globalization means promoting economic growth that is environmentally responsible, socially inclusive, and economically viable in the long term. By integrating sustainability into global trade, production, and consumption patterns, nations and businesses can help mitigate the negative effects of globalization on the environment. The goal is to ensure that the benefits of globalization are balanced with the need to protect the planet for future generations.
The Environmental Consequences of Globalization

While globalization has brought numerous economic benefits, it has also had significant environmental costs. The increased demand for resources, the expansion of global trade networks, and the acceleration of industrial production have all contributed to environmental degradation on a global scale. Understanding these consequences is key to finding solutions that can make globalization more sustainable.
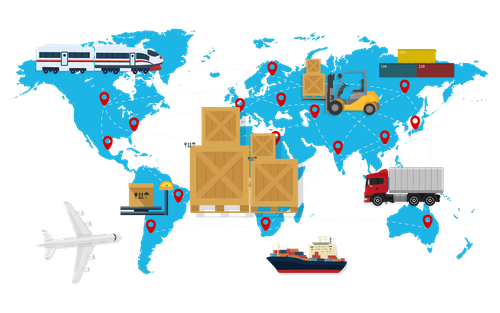
Carbon Footprint of Global Trade and Transportation
One of the most direct environmental impacts of globalization is the carbon footprint associated with global trade and transportation. The movement of goods across continents requires the use of ships, airplanes, trucks, and trains, all of which burn fossil fuels and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Shipping, which handles about 80% of global trade by volume, is a major contributor to carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, while aviation, though responsible for a smaller portion of goods transport, has a disproportionately high environmental impact due to the altitude at which emissions are released.
Global supply chains, which involve sourcing materials and components from multiple countries, have further increased the need for transportation. This interconnected system of production and distribution results in more emissions compared to localized production. As global trade continues to grow, so too does its environmental impact, making it crucial to find ways to decarbonize transportation and reduce the carbon footprint of international trade.

Deforestation and Resource Depletion
Globalization has also driven deforestation and the depletion of natural resources. To meet the increasing demand for commodities such as timber, palm oil, and soy, vast areas of forests have been cleared, particularly in tropical regions like the Amazon, Southeast Asia, and Central Africa. This deforestation contributes to the loss of biodiversity, disrupts ecosystems, and releases large amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere, further exacerbating climate change.
Moreover, the extraction of natural resources—such as minerals, fossil fuels, and water—has intensified due to the pressures of global consumption. The mining and drilling industries often cause environmental destruction, leading to soil erosion, water contamination, and habitat loss. As globalization fuels the demand for raw materials, unsustainable extraction practices threaten the long-term availability of these resources and the health of the planet.

Pollution and Waste Management Challenges
The rise of global industrialization and consumerism has led to increased pollution and waste, posing significant challenges for environmental management. Factories and manufacturing plants, especially in countries with less stringent environmental regulations, release pollutants into the air, water, and soil. These pollutants contribute to poor air quality, water contamination, and the degradation of ecosystems.
In addition to industrial pollution, the growing consumption of goods has resulted in more waste, particularly plastic waste. Single-use plastics, packaging materials, and electronic waste are often shipped to developing countries for disposal, overwhelming their waste management systems. As a result, many countries are grappling with severe pollution problems, including the accumulation of plastic waste in oceans, which has created vast “garbage patches” and threatened marine life. Addressing these waste management challenges requires both global cooperation and local action to reduce, reuse, and recycle materials more effectively.
Multilateral Agreements and Global Environmental Governance

Addressing the environmental consequences of globalization requires coordinated efforts at both the national and international levels. Multilateral agreements and global environmental governance play a crucial role in fostering cooperation among countries to tackle shared environmental challenges. These agreements establish common goals and frameworks that guide global efforts to mitigate climate change, protect ecosystems, and promote sustainable development.
The Paris Agreement: A Global Response to Climate Change
The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, is one of the most significant multilateral efforts to combat climate change. Nearly every country in the world has committed to this agreement, which aims to limit global temperature rise to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, with efforts to limit the increase to 1.5 degrees Celsius. The Paris Agreement sets out a framework for countries to establish their own national targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, known as nationally determined contributions (NDCs).
One of the strengths of the Paris Agreement is its flexible approach, allowing each country to tailor its emissions reduction plan based on its own economic and social conditions. However, the agreement also encourages transparency and accountability, requiring countries to report regularly on their progress. While the Paris Agreement is a critical step in global climate governance, its success depends on the political will and cooperation of all signatories to meet their commitments and take bold action against climate change.

The Role of the United Nations in Environmental Sustainability
Beyond the Paris Agreement, the United Nations (UN) plays a central role in advancing global environmental governance through a variety of initiatives. The UN’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, which includes the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), provides a comprehensive framework for promoting environmental sustainability alongside social and economic progress. Several of these goals, including those related to climate action, life below water, and life on land, directly address environmental issues.
The UN Environment Programme (UNEP) is the leading global authority on environmental issues within the UN system, coordinating international efforts to address challenges such as biodiversity loss, climate change, and pollution. Through initiatives like the UN Climate Change Conferences (COP), UNEP facilitates dialogue between governments, the private sector, and civil society to drive action on environmental sustainability. By providing platforms for international cooperation, the UN helps ensure that environmental governance remains a priority on the global agenda.

Regional Environmental Agreements and Initiatives
In addition to global agreements, regional environmental initiatives also play a key role in addressing localized environmental challenges. The European Union (EU) has been at the forefront of regional environmental governance with its European Green Deal, which aims to make Europe the first climate-neutral continent by 2050. The EU’s ambitious policies target emissions reduction, energy efficiency, and the transition to a circular economy.
Similarly, other regions have developed their own environmental frameworks. For example, the African Union has implemented the African Strategy on Climate Change, focusing on climate adaptation and sustainable land management. In Southeast Asia, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is working on regional environmental initiatives, particularly in managing transboundary pollution and protecting biodiversity.
These regional agreements are vital for addressing the specific environmental issues that different regions face. By complementing global efforts, they ensure that environmental sustainability is pursued at both the regional and global levels.
Corporate Responsibility and Sustainable Practices

As globalization has expanded, multinational corporations (MNCs) have emerged as key players in the global economy. These corporations, due to their global reach and influence, bear a significant responsibility for the environmental impacts of their operations. Increasingly, businesses are recognizing the importance of integrating sustainability into their strategies, not only to reduce their environmental footprints but also to meet the growing demands of consumers, investors, and regulators for more sustainable business practices.

The Role of Multinational Corporations in Promoting Sustainability
Multinational corporations are in a unique position to drive sustainability on a global scale. As companies that operate across multiple countries and regions, MNCs have the resources, influence, and capacity to implement environmentally sustainable practices across their global supply chains. By adopting green practices—such as reducing emissions, minimizing waste, and using renewable energy—corporations can significantly mitigate their environmental impacts.
Moreover, MNCs are increasingly realizing that sustainability is not just a matter of corporate social responsibility (CSR) but also a business imperative. Consumers and investors are demanding greater transparency and accountability from companies regarding their environmental performance. As a result, many global brands are incorporating sustainability goals into their core business strategies. For example, companies like Unilever, Tesla, and Patagonia have made significant commitments to sustainability, from using eco-friendly materials to pledging carbon neutrality.
However, the challenge remains in ensuring that sustainability commitments are implemented consistently across all operations, particularly in developing countries where environmental regulations may be weaker. As MNCs continue to expand globally, ensuring that they uphold sustainability standards across all markets is essential for creating long-term environmental benefits.
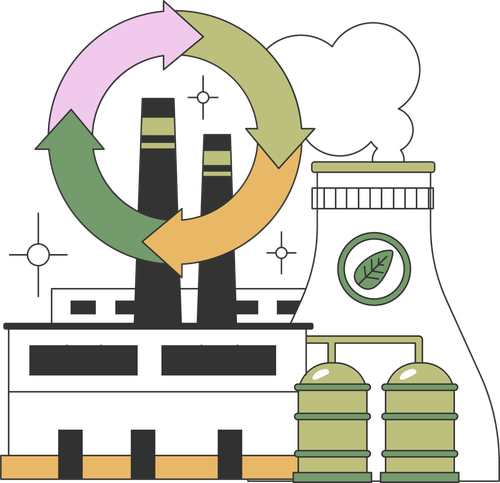
Circular Economy: Reducing Waste and Increasing Resource Efficiency
The concept of a circular economy has gained traction as a solution to the growing problem of waste and resource depletion. In contrast to the traditional linear economy, where resources are extracted, used, and discarded, the circular economy focuses on keeping products, materials, and resources in use for as long as possible. This is achieved through strategies such as recycling, reusing, and remanufacturing products, as well as designing goods for longevity and repairability.
By embracing circular economy principles, companies can reduce their environmental impact while also improving efficiency and lowering costs. For example, global furniture giant IKEA has committed to becoming a fully circular business by 2030, focusing on using renewable and recycled materials and designing products that can be reused or repaired. Similarly, companies in the electronics sector are exploring ways to extend the lifespan of devices and reduce electronic waste through repair and recycling programs.
The circular economy not only addresses the issue of waste but also helps reduce the demand for virgin resources, decreasing the environmental pressure on ecosystems and biodiversity. As more companies adopt circular practices, the global economy can transition toward a more sustainable model of production and consumption.
Green Technologies and Innovations
Technological innovation is a key driver of sustainability in the globalized world. Green technologies, such as renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and green building practices, are transforming industries and reducing environmental impacts. Solar, wind, and hydropower technologies have made significant strides, providing cleaner alternatives to fossil fuels and helping countries transition to a low-carbon economy.
In agriculture, innovations such as precision farming and sustainable land management practices are reducing the environmental footprint of food production while improving yields. Meanwhile, green building technologies—such as energy-efficient materials, smart grids, and sustainable water management systems—are helping cities and businesses reduce their energy consumption and environmental impact.
As the global demand for green technologies grows, innovation will continue to play a critical role in the transition to a sustainable future. Businesses that invest in green technologies not only contribute to environmental sustainability but also position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly eco-conscious global market.
Solutions for a Sustainable Global Economy

Creating a sustainable global economy requires more than just corporate responsibility and green technologies—it demands a systemic shift in how industries, governments, and consumers interact with the environment. Implementing wide-scale solutions to decarbonize industries, promote sustainable consumption, and align global goals with sustainability frameworks like the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is essential to making globalization sustainable in the long term.

Decarbonizing Global Industries
One of the most urgent solutions for creating a sustainable global economy is decarbonizing key industries such as energy, transportation, and manufacturing. These sectors are among the largest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, and transitioning them to low-carbon models is critical for addressing climate change.
The energy sector is undergoing a significant shift as renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power replace fossil fuels. Governments and businesses are investing in clean energy technologies to reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the environmental impacts of traditional energy production. Countries like Germany and Denmark have set ambitious goals to transition to 100% renewable energy, and companies like Tesla and Vestas are leading the way in renewable energy innovation.
In the transportation sector, electric vehicles (EVs) and advances in battery technology are reducing the carbon footprint of global transportation networks. Companies like Tesla, BYD, and major automotive manufacturers are scaling up EV production, while governments are introducing policies to promote the adoption of cleaner vehicles and invest in charging infrastructure. These efforts are essential for reducing the carbon emissions associated with global trade and travel.
Decarbonizing industries also involves increasing energy efficiency, reducing waste, and adopting sustainable manufacturing practices. Technological innovations, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS), offer potential solutions for industries like cement and steel, which are traditionally hard to decarbonize. These advancements will be crucial in achieving the global emissions reduction targets set out in the Paris Agreement.
Promoting Sustainable Consumption and Production
Sustainable consumption and production patterns are central to achieving a sustainable global economy. Encouraging businesses and consumers to adopt sustainable practices requires a combination of regulatory measures, incentives, and public awareness campaigns. Governments can play a significant role by implementing policies that promote sustainable products, reduce waste, and encourage the use of eco-friendly alternatives.
On the production side, businesses must focus on sustainable sourcing, manufacturing, and distribution practices. This includes reducing the use of hazardous materials, minimizing energy consumption, and adopting circular economy principles. Companies that embrace sustainable production not only reduce their environmental impact but also gain a competitive advantage in a market where consumers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability.
For consumers, shifting towards sustainable lifestyles involves making conscious choices about the products they purchase, reducing waste, and supporting companies that prioritize sustainability. This includes reducing consumption of single-use plastics, buying energy-efficient appliances, and opting for products made from sustainable materials. Public awareness campaigns and labeling initiatives, such as the Fair Trade label or the EU Ecolabel, can help consumers make informed decisions that support sustainable practices.

Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and Global Collaboration
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a comprehensive framework for achieving sustainability on a global scale. The 17 SDGs address a wide range of social, economic, and environmental challenges, with specific goals dedicated to climate action, life below water, and life on land. By aligning global efforts with the SDGs, countries can work collaboratively to achieve sustainable development that benefits both people and the planet.
Global collaboration is key to achieving the SDGs, as many environmental challenges—such as climate change, deforestation, and ocean pollution—are transboundary issues that require coordinated action. Multilateral agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, and initiatives like the Green Climate Fund are examples of how global cooperation can drive progress toward sustainability. In addition, partnerships between governments, businesses, and civil society are essential for ensuring that the SDGs are effectively implemented at all levels.
By focusing on sustainable development, the international community can create a future where economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection go hand in hand. Achieving the SDGs will require continued innovation, investment, and collaboration to address the pressing environmental issues that threaten the planet and its people.
Balancing Economic Growth with Environmental Responsibility

The relationship between globalization and the environment is complex. While globalization has driven unprecedented economic growth and interconnectedness, it has also contributed to environmental degradation. As the world moves forward, balancing economic growth with environmental responsibility is critical to ensuring a sustainable future. Globalization can no longer be pursued at the expense of the environment; instead, it must evolve to support long-term sustainability goals.

The Need for Global Cooperation on Sustainability
Achieving sustainability in the context of globalization requires collective action at all levels—local, national, and international. Governments, corporations, and individuals must work together to address the pressing environmental challenges facing the planet. Global cooperation, through multilateral agreements and international organizations, is essential for creating a framework that supports sustainable economic development and environmental protection. Initiatives like the Paris Agreement and the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are examples of how countries can collaborate to create a more sustainable global economy.

The Future of Sustainable Globalization
Looking ahead, the future of globalization must prioritize sustainability. By embracing renewable energy, circular economies, sustainable production practices, and green technologies, the global community can transition to a model of globalization that promotes both economic growth and environmental stewardship. Innovation and investment in sustainable practices will be key to addressing the environmental challenges posed by globalization while creating new opportunities for industries, businesses, and communities.
As global awareness of environmental issues continues to grow, there is a growing sense of urgency to integrate sustainability into all aspects of the global economy. With the right policies, technologies, and collaborative efforts, it is possible to create a future where globalization and sustainability are not in conflict but instead work hand in hand to create a more equitable and resilient world.

Link to Next Episode: Global Supply Chains
The next episode, “Global Supply Chains: Challenges and Opportunities,” will explore the intricate network of global supply chains and the challenges they face in the modern world. From disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions to the opportunities for building more resilient and sustainable supply chains, this episode will discuss the future of global trade and the innovations needed to support a rapidly changing global economy.
FAQs
-
How does globalization impact the environment?
Globalization impacts the environment in various ways, including increased carbon emissions from transportation, deforestation due to expanded agriculture, and pollution from industrial activities. While it promotes economic growth and development, globalization also puts pressure on natural resources and contributes to environmental degradation if not managed sustainably.
-
What is the relationship between globalization and climate change?
Globalization contributes to climate change by driving higher energy consumption, industrial production, and international transportation, all of which increase greenhouse gas emissions. However, it also facilitates the spread of climate solutions, such as renewable energy technologies, global environmental standards, and international agreements aimed at reducing emissions.
-
How does international trade affect environmental sustainability?
International trade can both harm and help environmental sustainability. On the negative side, it often leads to increased production and consumption, contributing to resource depletion and pollution. On the positive side, trade can enable the global distribution of green technologies, promote sustainable production standards, and encourage countries to adopt environmentally friendly practices through trade agreements.
-
What are the environmental benefits of a circular economy in globalization?
A circular economy reduces waste and maximizes resource efficiency by promoting recycling, reusing, and repurposing materials. In a global context, this approach can significantly lower the environmental impact of production and consumption by minimizing raw material extraction, reducing pollution, and extending product lifecycles. Globalization allows the circular economy principles to be shared and implemented across borders.
-
How do multinational corporations (MNCs) address sustainability in their operations?
Multinational corporations address sustainability through various strategies, such as adopting eco-friendly technologies, reducing carbon footprints, and implementing sustainable supply chain practices. Many MNCs set sustainability goals, like net-zero emissions or zero waste, and report their environmental impact publicly. They also engage in corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives to improve their environmental performance globally.
-
What role do international agreements play in promoting sustainability?
International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement on climate change and the Kyoto Protocol, play a critical role in promoting sustainability by setting targets for carbon reduction and encouraging countries to adopt sustainable practices. These agreements facilitate global cooperation, provide frameworks for environmental action, and hold nations accountable for their commitments to reduce environmental impact.
-
How can globalization support the spread of green technologies?
Globalization supports the spread of green technologies by facilitating international collaboration, investment, and trade in sustainable innovations. Technologies such as solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicles benefit from global markets and supply chains, allowing them to scale up and become more affordable. This cross-border exchange accelerates the adoption of clean technologies worldwide.
-
8. How does sustainable finance influence environmental practices in globalization?
Sustainable finance, including green bonds and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investing, directs capital toward projects and companies that prioritize sustainability. This approach encourages businesses to adopt greener practices by providing financial incentives and holding them accountable to environmental standards, thus aligning economic globalization with sustainable development goals.
-
What challenges do developing countries face in implementing sustainable practices in a globalized world?
Developing countries often face challenges such as limited access to technology, insufficient funding, and weak regulatory frameworks that hinder the implementation of sustainable practices. While globalization can provide access to new technologies and international funding, these countries need targeted support to build capacity, enforce environmental laws, and transition to sustainable economic models.
-
What are some innovative solutions to reduce the environmental impact of globalization?
Innovative solutions to reduce the environmental impact of globalization include adopting renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, promoting sustainable agriculture, and implementing carbon pricing mechanisms. Additionally, technologies like blockchain can enhance supply chain transparency, helping companies track their environmental impact and make more sustainable choices.














